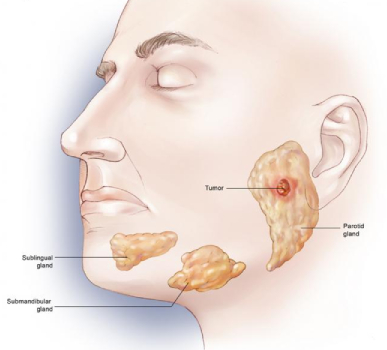
What is Parotid Tumor?
Cancer starts when cells begin to grow out of control. Parotid tumor is a type of tumor that forms in the parotid glands - major salivary gland in humans, which makes saliva and releases it into the mouth. The two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both the ears. Most of the salivary gland tumors begin in the parotid glands. Most often the parotid tumor can be cured with the treatment.
What causes parotid tumor?
It is not clear what exactly causes the parotid tumor. Causes could be smoking, and exposure to radiation. Parotid tumor does not usually run in families, so most of the DNA changes that lead to this cancer are not likely to be inherited from a person's parents. Instead, these changes probably take place during a person's lifetime. Sometimes the cause might be something specific, like exposure to radiation or certain cancer-causing chemicals.
We at CAN-C provide parotid tumor treatment in Bangalore.
Here, you will find information about signs and symptoms, causes and risk factors, types, diagnosis, staging about parotid tumor/parotid cancer.
Parotid tumor can cause any of the following signs or symptoms:
A lump or swelling cheek, or neck
Pain in the mouth, cheek, jaw, ear, or neck that does not go away
A difference in the size and/or shape of the left and right sides of the face or neck
Numbness in part of the face
Weakness of the muscles on one side of the face
Trouble in opening the mouth widely
Fluid draining from an ear
Trouble swallowing
A risk factor is anything that increases a person's chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Different types of cancers have different risk factors. Some risk factors can be changed, like smoking. Some risk factors cannot be changed like a person's age or family history. There is no surety that a person having risk factor could essentially have the disease or those without risk factors will never get the disease.
Male gender: Parotid tumor/cancer more in men than in women.
Radiation exposure: Radiation to the head and neck area, if ever, also increases the risk of parotid tumor.
Workplace exposure to certain radioactive substances or with certain metals or minerals, asbestos mining, plumbing, rubber factories, some forms of wood work also increases the risk of parotid tumor, but extremely rare cases.
Tobacco and alcohol, might increase the risk, though they have not been strongly linked to parotid tumor in most studies.
CAN-C: Best centre for parotid cancer treatment in Bangalore.
The main types of parotid tumor are
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma: The most common type is mucoepidermoid carcinoma. In this form of tumor they often form tiny mucous-filled cysts. Most mucoepidermoid carcinomas develop in the parotid glands. These are usually low grade, but they can sometimes be high grade.
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: This form of tumor is a very aggressive. As this often grows along the nerves, it causes pain and facial paralysis. They have high propensity to recur.
Acinic Cell Carcinoma: This tumor develops in the acinar cells, which produce saliva. These are also low grade tumors. They are more commonly seen in women than in men.
Polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma (PLGA): Polymorphous means the cancerous tissue has a variety of different growth patterns when seen under a microscope. Although rare, still the second most common cancer after the adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma, NOS (Not Otherwise Specified): These are high grade tumours and must always be differentiated from a metastatic foci from else where in the body
Parotid tumor may be diagnosed after a person goes to a doctor because of symptoms, or it might be found during a routine physical exam or other tests. If there is a reason to suspect parotid tumor, the doctor will use one or more tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Medical history and physical exam
Most often the first step in diagnosing cancer is to take medical history. The doctor will ask about the symptoms and when they first appeared. They may even ask about the risk factors for the parotid tumor and about the general health.
As regards to the physical exam, the doctor will carefully examine mouth and the areas around the mouth, the sides of face, and around the ears and jaw. The doctor will also check for lump, numbness or weakness in the face.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests use x-rays(CT Scan), magnetic fields (MRI), or radioactive particles(PET CT) to create pictures of the inside of the body. Imaging tests are done for a number of reasons such as to find a suspicious area that could be cancerous, to learn how far it has spread, and also to help find if the treatment has been effective.
a. Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan
A CT scan uses x-rays to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Unlike a regular x-ray, CT scans can show the detail in soft tissues. A CT scan can show the size, shape, and position of a tumor and can help find enlarged lymph nodes that might contain cancer. If needed, CT scans can also be used to look for tumors in other parts of the body.
b. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
MRI scans make detailed images of soft tissues in the body and have better soft tissue delineation than CT Scan and hence most preferred imaging modality to evaluate parotid gland. But MRI scans use radio waves and strong magnets instead of x-rays. The energy from the radio waves is absorbed and then released in a pattern formed by the type of body tissue and by certain diseases. A computer translates the pattern into very detailed images of parts of the body. MRI scans can help determine the exact location and extent of a tumor. They can also show any lymph nodes that are enlarged or if other organs have suspicious spots, which might be due to the spread of cancer.
c. Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
This test can help show whether an abnormal lump or tumor seen on another imaging test may harbour cancer. If you have been diagnosed with cancer, your doctor may use this test to see if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Biopsy
When the symptoms, exam results, imaging tests all suggest a parotid tumor, then the actual diagnosis is made by removing cells from an abnormal area and looking at them under a microscope. This method is known as a biopsy.
a. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy
FNA biopsy is a procedure where in a fine needle used to aspirate a small amount of cells and fluid from the lump for testing. This type of biopsy can be done in a doctor's office or clinic. After performing the biopsy, the sample is sent to the lab to look for cancer cells.
b. Incisional biopsy
This type of biopsy are rarely done for parotid tumor. Only in situations where the FNA biopsy has not provided a large enough sample, this option is opted.
Surgery
Most often the FNA biopsy may not provide clarity. In such instances where the physical exam and imaging tests suggest tumor, but the FNA is not clear, the doctor may opt for surgery to remove the tumor completely. As this provides sample for the diagnosis as well as treat the tumor at one go.
The tests and diagnosis will help determine the parotid tumor and how far it has spread from parotid to the other parts.
Clinical assessment and Imaging modalities aid in staging the tumour
How is the stage determined?
TNM staging system is the most commonly used method to describe the different stages of parotid tumor, which is based on 3 key pieces of information:
The extent (size) of the tumor (T): How large is the tumor? Has it grown into nearby structures?
The spread to nearby lymph nodes (N): Has the tumor spread to nearby lymph nodes?
The spread (metastasis) to distant sites (M): Has the tumor spread to the distant organs such as the lungs?
CAN-C: Well-known centre for parotid tumor treatment in Bangalore.
"CAN-C: Expert specialists in parotid tumor treatment in Bangalore."
Make An Appointment Today
How Parotid Tumor is treated?
When diagnosed with parotid tumor, it is very important to know all the treatment options at hand, weigh the pros and cons of each treatment option and then come to a conclusive decision. There are a few ways to treat parotid cancer. The treatment provided depends on the type and the stage of the cancer. It also depends on various other factors like age, overall health, and many other things that distinguish one person to another. Most often parotid tumor can be cured with treatment.
Surgery of the parotid gland is challenging, as the facial nerve runs through the gladular substance of parotid, dividing the gland into superficaial and deep lobe. Facial nerve supplies all muscles of facial expression and its sacrifice adds on to significant morbidity. However, tumour clearance is paramount in achiveing good oncologic outcomes and hence at times when facial nerve is resected, various static and dynamic reconstructive and rehabilitation methods exist to decrease the morbidity of facial paralyisis.
Types of surgery for parotid tumor.
1. Superficial parotidectomy
Most of the salivary gland tumors occur in the parotid gland. Most parotid gland tumor start in the outside part of the gland, called the superficial lobe. These can be treated by removing only this lobe, which is called a superficial parotidectomy. This usually leaves the facial nerve intact and does not affect facial movement. This suegry is usually performed to remove benign parotid tumours.
2. Total parotidectomy
If the cancer has spread into deeper tissues, the surgeon will remove the entire gland. This is called a total parotidectomy. When whole gland is removed with facial nerve preservation then surgery is termed conservative total parotidectomy.
3. Lymph node removal (neck dissection)
Surgery to remove lymph nodes is called a lymph node dissection or lymphadenectomy. Parotid tumor sometimes spread to lymph nodes in the neck (cervical lymph nodes), and these may need to be removed as a part of treating the tumor. This is called a neck dissection.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays or particles to destroy cancer cells or slow their growth.
It is commonly used after surgery to try to kill any cancer cells that might have been left behind to help reduce the risk of cancer coming back.
It can also be used sometimes in people with advanced parotid tumor not amenable for surgery to control symptoms such as pain, bleeding, or trouble swallowing.
External beam radiation therapy is the type of radiation therapy which is most often used to treat parotid tumor/cancer. This focuses radiation from outside the body on the cancer.
Most often, radiation treatments are given 5 to 6 days a week. The length of treatment and frequency depends upon the reason radiation is used, i.e., may be shorter if the radiation is being used to relieve symptoms from cancer spread than treat cancer itself.
There are new advanced forms of radiation therapy such as the 3D-CRT, Fast neutron beam radiation, and IMRT. Many major hospitals and cancer centers now use IMRT as the standard way to deliver external beam radiation.
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the treatment with anti-cancer drugs that are given into the vein or by mouth. These drugs enter the bloodstream and reach all areas of the body, making this treatment useful for cancers that have spread beyond the head and neck. Though this is not often used to treat parotid tumor. It is used in instances where the cancer has metastasized to distant organs or if the option of surgery and radiation therapy is ruled out. Though chemo sometimes shrinks the tumors, it does not cure this type of cancer.
Some of the chemo drugs used to treat parotid tumor include:
1. Cisplatin
2. Carboplatin
3. Doxorubicin
4. 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)
5. Cyclophosphamide
6. Paclitaxel
7. Docetaxel
8. Vinorelbine
Most often these drugs are given in combinations of either 2 or more drugs, but may be used alone also. As parotid tumors are not common, the best way to use chemotherapy to treat the parotid tumor is not yet clear.
There is a recent advancement in targetted therapy for managing unresectable and distant metastatic tumours of the parotid gland. The targetted therapy will be recommened based on the pathological tumour type and expression of the molecular target by the tumour.
